The purpose of organic farming is not to negate and reject the positive achievements of conventional agriculture, but to find better environmental solutions where it is most needed. Organic agriculture is a part of modern agricultural production, trade and agronomic science and it is based on its latest knowledge and achievements.
Organic (ecological, biological) agriculture is the production without the usage of agrochemicals (mineral fertilizers, synthetic plant protection products, hormones, etc.). The purpose of organic farming is not to negate and reject the positive achievements of conventional agriculture, but to find better environmental solutions where it is most needed. Organic agriculture is a part of modern agricultural production, trade and agronomic science and it is based on its latest knowledge and achievements.
The basic principles of organic farming are:
a) Harmonization and proper management of fertilization, crop rotation, diversity and choice of crops, varieties and breeds, tillage, and strengthening of disease and pest resistance. In particular, it seeks to stimulate the activity of biological processes within the economy itself, involving micro-organisms and wildlife;
b) care for the proper maintenance of the soil, the preservation and enhancement of its fertility and biological activity, the content of organic matter and nutrients, and the improvement of soil structure and the fight against erosion;
c) Management that excludes, or only exceptionally permits, the use of agrochemicals (mineral fertilizers, synthetic plant protection products, synthetic growth regulators, hormones, etc.);
d) Preserving the diversity of plant and animal species in nature (combating “genetic erosion”), as well as conserving other natural resources (e.g. groundwater) and landscape diversity;
e) The production of better quality and therefore more nutritionally duly foods;
f) Achieve satisfactory economic success for the farm;
g) Reducing and minimizing energy consumption, i.e. fossil fuels;
h) Developing healthy social impulses among people;
g) Nurturing an understanding of nature, its rhythms and laws;
h) Creating a link for a new, different relationship between man and nature, based on the principles of spirituality and holism, not materialism and reductionism.
Organic farming is a system of agricultural management that strives for ethically acceptable, environmentally friendly, socially fair and economically viable agricultural production.
Basics of organic production:
– Preservation of soil fertility with sources on the farm itself, such as: cultivation of forage legumes, green fertilization, use of manure, compost, preparation of biological products on the farm, rational way of cultivation of soil, biological control of weeds, etc. The cultivation of legumes in the soil leaves 150 to 300 kg of nitrogen (N) per hectare of surface area, while intermediate crops can leave 2 to 4 tons of organic matter and at the same time clean the soil from weeds, make better use of P and K (husk, rauola), or tillage with a lower frequency of preserves humus, fruiting takes on a phytosanitary dimension, without chemistry, with cultivation and mulching against weeds.
In 2018, 4,374 organic farming entities were registered in the Republic of Croatia. The number of organic farmers in 2018 has increased by almost 9% compared to 2017. This is an increase of 351 organic farmers compared to last year. Area under organic production in 2018 was 103 166 ha, which is 6.94% of the total agricultural production.
An “organic product” is a product with 95% or more organic ingredients. This 5% is left in the case of atmospheric pollution such as acid rain or pesticides brought from the wind by an adjacent property, etc. It is defined what all goes into these 5%, e.g. it is not possible to sweeten the marmalade with white refined sugar because then loses its consistency, but it must be natural ingredients but not certified, such as water that cannot be certified, this is prescribed by The Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Rural Development (MAFRD). The organic product must have all the ingredients listed on the label.
A producer in organic production is a legal or natural person who produces organic products, processes, or trades organic products, and is entered in the Register of producers in organic production of agricultural and food products. “Organic production unit” means an entire economy or part of an economy, clearly separated from every other unit, and produced in accordance with the provisions of the Organic Production of Agricultural and Food Products Act and the regulations made thereunder.
The organic product is labeled with “organic product label”, which is a unique prescribed label for products produced in accordance with the Law on Organic Production of Agricultural and Food Products and the regulations made thereunder. Organic farming is defined by the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM) and accepted in the programs of the United Nations (WHO and FAO) and of the Council of the European Union (Council Regulation 2092/91 of 24 June 1991), where it is carried out in accordance with specific standards and regulations, and the FAO / WHO common working group at the UN works on guidelines for the production of organic food (Food Regulations). Croatia has accepted international standards and accepted a package of laws and regulations governing organic production.
The Paying Agency for Agriculture, Fisheries and Rural Development (PAAFRD) annually issues Measure 11 Organic farming. It aims to encourage new farmers to become involved in this production system, those who are already in the organic production system to continue their activities in order to increase the area under organic production. This will reduce the negative impact of conventional agriculture on the environment by maintaining water, air and soil quality, as well as increasing soil fertility. Organic farming contributes to human health and animal welfare. By accepting prescribed farming practices and methods that go beyond the baseline, the farmer is paid increased costs or lost income compared to normal agricultural production. Support can be achieved through two sub-measures: 11.1. Payments for the transition to organic farming practices and methods and 11.2. Payments for maintaining organic farming practices and methods. For more information on these measures, click on link https://www.apprrr.hr/measure 11-environmental-rearing/.
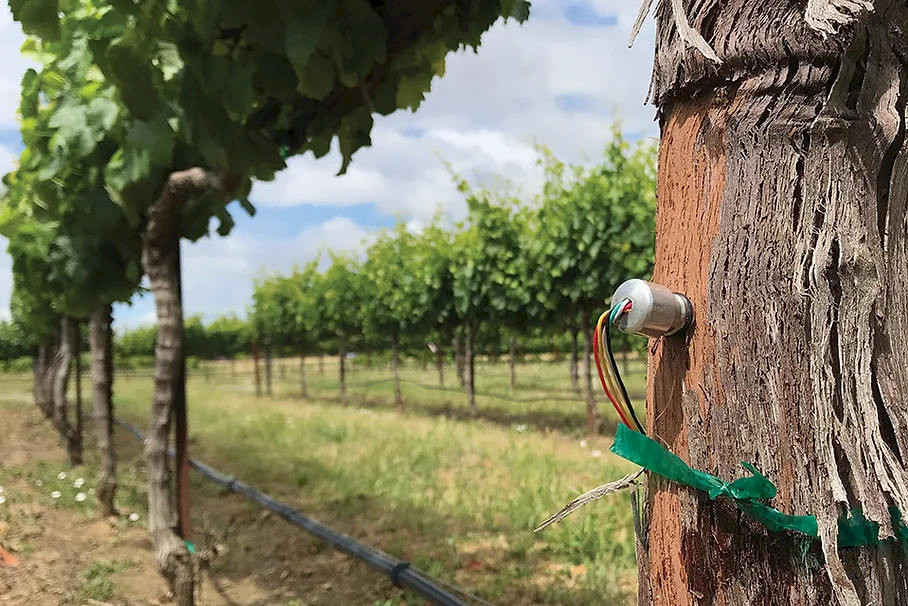
To make organic farming as successful as possible, the Pinova Meteo professional agriculture weather station greatly helps. Pinova Meteo is a reliable professional agriculture weather station that answers many questions that producers face in their daily agricultural production. The station saves time, money and resources! There is no need to collect process and analyze data manually. The station also comes with a computer and mobile application through which you can quickly access data from your plantation. The professional agriculture weather station is used by fruit growers, vineyards, vegetable growers, nurseries and growers, whether for organic, integrated or conventional production. Prognostic models of plant diseases are of great help in plant protection planning.
For more information about the Pinova Meteo Station, visit the following link: https://pinova-meteo.com/en/products-and-services/pinova-meteo-agriculture-weather-station
Sara Spahija, mag. ing. agr.
References:
https://pinova-meteo.com/en/products-and-services/pinova-meteo-agriculture-weather-station
Znaor, D, 1996: Ekološka poljoprivreda, Globus, Zagreb
Kisić, I, 2014: Uvod u ekološku poljoprivredu, Agronomski fakultet Sveučilišta u Zagrebu
https://www.apprrr.hr/mjera-11-ekoloski-uzgoj/
https://www.dzs.hr/